Piping systems are a crucial part of many industries, including oil and gas, chemical, and food processing. These systems transport fluids, such as liquids, gasses, or slurries, from one point to another. However, as these fluids move through the piping system, they may contain solid particles or debris that can damage equipment or clog pipelines. The incomparable significance of strainers in the seamless operation of piping networks cannot be emphasized enough. Their indispensable role lies in the elimination of covert contaminants that may trigger the malfunctioning of such intricate systems. The intricate nuances of the various types of strainers in piping can often leave one feeling bewildered. And the task of selecting the appropriate strainer can be a daunting one.
Fear not, as we have meticulously compiled a comprehensive guide that is sure to demystify the complexity surrounding strainers in piping systems.
What is a Strainer?
The tool known as a strainer is an essential component in the filtration of unwanted impurities, particles, and debris from a variety of fluid mediums, such as liquids, gases, and slurries. Its paramount role cannot be overstated, as it aids in ensuring the purity and quality of the filtered substance. These strainers are typically composed of a perforated or mesh screen that is designed to trap solid particles and contaminants. While still allowing the fluid to pass through. They are widely used in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing. To safeguard downstream equipment, maintain product quality, and preserve system efficiency.
In the ever-evolving market of today, one can find a plethora of types of strainers in piping, each with its unique filtration purpose. From the widely-used Y-strainers and basket strainers to the more specialized duplex strainers, temporary strainers, and cone strainers, the choices are endless. Choosing the most fitting strainer for any particular application depends solely on the specific requirements of the said application. With so many options available, the decision-making process can be perplexing. But with careful consideration, the ideal strainer can be selected to achieve optimal filtration results.
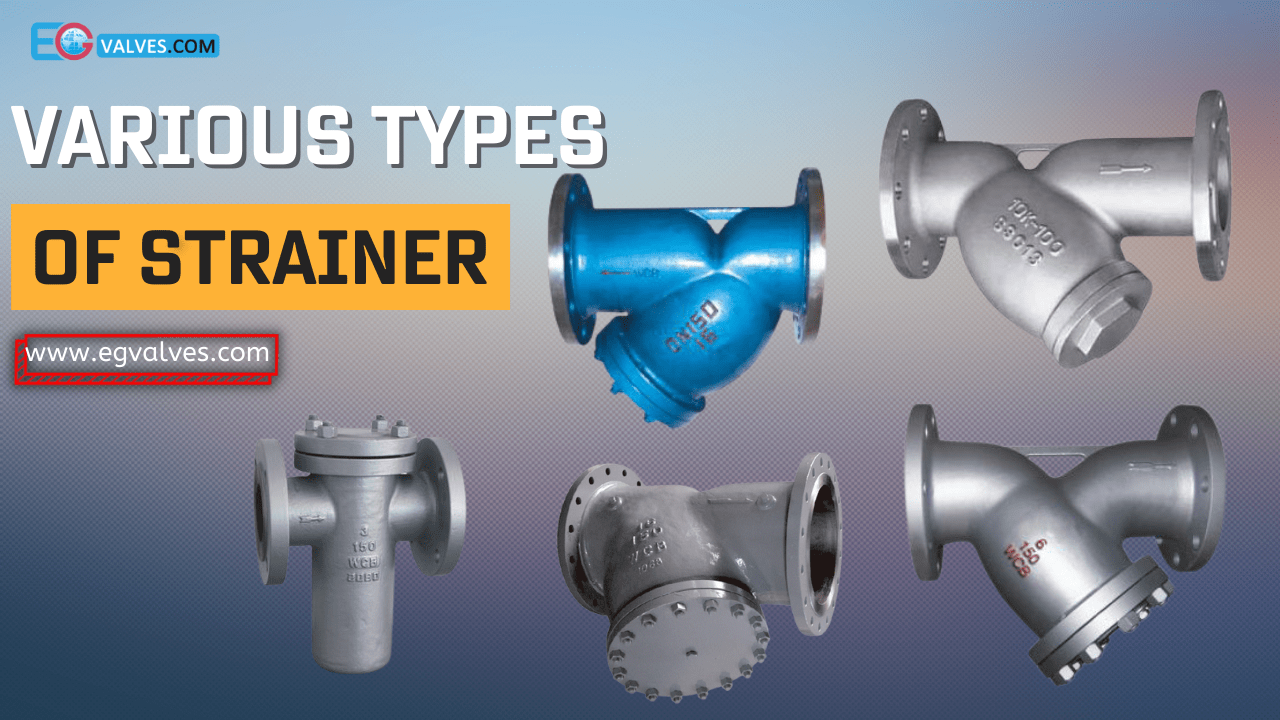
Types of Strainers in Piping:
Strainers are crucial components in maintaining the smooth operation of piping systems and protecting downstream equipment from potential harm caused by unwanted solid particles, debris, and impurities. Without strainers, these contaminants can cause clogging, erosion, corrosion, and other forms of damage to the piping system and its components. They guarantee that the final product’s quality remains uncompromised while ensuring that the system runs at peak efficiency.
A vast assortment of strainers is available for purchase on the market, with each strainer type possessing distinct features and benefits that render them suitable for a variety of applications. Here are some of the most commonly used types of strainers in piping systems:
- Y-Strainers
- Basket Strainers
- Duplex Strainers
- Temporary Strainers
- Cone Strainers3
-
Y-Type Strainers:
Y-type strainers are a specific type of strainer that has been specially designed to remove small granules from the medium flowing through a piping system. They are commonly used in piping systems that allow for regular maintenance to improve efficiency. Y-type strainers can be installed horizontally or vertically, depending on the specific requirements of the application. They are commonly used in pipelines with high-pressure levels exceeding 6000 PSI, where the risk of damage from unwanted particles and debris is significant. The strainer gets its name from its shape, which resembles the letter “Y”.
The Y-type strainer is equipped with two openings and a diagonal drain pipe to flush out debris. Any trash or debris is captured by the strainer before being expelled. It is generally recommended to install Y-type strainers vertically to prevent erosion, especially when the fluid being filtered is a liquid. In instances where filtration of gas or vapor is necessary, a strainer may be installed either horizontally or vertically based on the specific requirements of the application.
It is imperative to note that Y-type strainers are not intended to manage significant quantities of dirt or particles and necessitate regular cleaning to prevent blockages.
-
Basket-type Strainers:
In contrast to Y-type strainers, basket-type strainers have a different structure and are intended to filter out larger-sized particles. They are suitable for pipelines that require frequent cleaning and are often used in applications with a pressure of up to 1,500 PSI. Basket strainers have been designed for installation only in parallel pipes and demand additional reinforcement due to their more substantial structure.
Basket strainers are well-suited for applications that require the retention of a larger volume of particles and decreased frequency of cleaning. Due to their larger straining area, they are capable of capturing a greater number of particles.
It is essential to note, however, that basket strainers have a lower capacity for pressure reduction than Y-type strainers. The cover located on top of the basket strainer can be easily removed, allowing the operator to clean the strainer or replace the filter element when debris begins to accumulate.
-
Duplex Strainers:
Duplex strainers operate using two filtering elements that work together to filter the medium. While they share some similarities with basket strainers, they also have distinct differences. Duplex strainers are particularly useful in situations where cleaning between processes is difficult due to continuous operation. With two strainers in place, when one becomes full, the medium flow is automatically directed to the other strainer, ensuring uninterrupted operation. This ensures that the filtering process is uninterrupted until the first strainer can be cleaned or replaced.
Typically, duplex strainers come equipped with plug or ball-type valves. Which allows for the flow of the medium to be redirected from one strainer to the other. Duplex strainers may only be installed in parallel pipelines and are well-suited for larger pipes. They are most effective in continuous pipelines or processes, as one strainer can take over while the other is being cleaned or replaced.
-
Tee Strainers:
Tee strainers, also known as T-strainers, are a type of strainer used in piping systems. To remove unwanted debris or particles from fluids. As the name suggests, the strainer is shaped like a “T” and is installed perpendicular to the flow direction of the fluid.
Tee strainers are typically used in applications where the flow rate is low and the amount of debris to be removed is minimal. They are designed to handle low-pressure applications. And can be used with a wide range of fluids, including gases, liquids, and steam.
Tee strainers consist of a body with a flanged inlet and outlet and a removable screen or filter element. The fluid enters through the inlet and flows through the
screen or filter element, which captures any debris or particles in the fluid. The filtered fluid then exits through the outlet.
One advantage of tee strainers is their compact size. Which makes them ideal for use in tight spaces or where there is limited installation space. However, they may require more frequent maintenance compared to other types of strainers, as the screen or filter element can become clogged quickly, especially in applications with high levels of debris.
Overall, tee strainers are a useful option for low-flow applications that require basic filtration of fluids in a compact package.
-
Cone Strainers:
Cone strainers are used in applications where a high level of filtration is required. They are installed in a vertical position and have a conical-shaped screen that traps solid particles and debris. The conical shape of the screen allows for a large filtration area, which reduces the frequency of cleaning.
When Choosing the Right Strainer, things to consider:
Choosing the right strainer for your specific application requires careful consideration of multiple factors. These factors include the flow rate, pressure, temperature, and the size and type of particles that need to be removed. Here are some of the essential factors to keep in mind when selecting the right strainer for your application:
1. Flow Rate:
The flow rate refers to the volume of fluid that passes through the system per unit of time. And selecting a strainer that matches this rate is essential for ensuring efficient filtration and preventing damage to downstream equipment. The strainer should be able to handle the maximum flow rate without causing a significant pressure drop. A strainer with a lower flow rate may quickly become clogged, requiring more frequent cleaning and maintenance. Therefore, selecting a strainer that can handle the flow rate of your fluid is critical for achieving optimal performance and avoiding costly downtime.
2. Pressure:
The pressure of the fluid in the piping system is another critical factor to consider when choosing a strainer. The strainer should be able to withstand maximum pressure without leaking or failing. The pressure drop across the strainer should also be considered, a high-pressure drop. This can result in reduced flow rates and increased energy costs.
3. Temperature:
The temperature of the fluid in the piping system is another important factor to consider when selecting a strainer. The strainer should be able to withstand the maximum temperature without melting or deforming. The temperature can also affect the viscosity of the fluid. which can impact the strainer’s ability to filter out particles effectively.
4. Particle Size:
The size and type of particles that need to be removed from the fluid are also essential factors to consider when selecting a strainer. Different types of strainers have different screen sizes and mesh options, which can filter out particles of varying sizes. For example, Y-type strainers typically have a mesh size ranging from 20-400 microns, while cone strainers can filter particles as small as 10 microns.
Knowing the particle size and type is critical in selecting the right strainer to prevent damage to downstream equipment and ensure the quality of the end product.
5. Maintenance and Cleaning:
Maintenance and cleaning requirements are also crucial factors to consider when selecting a strainer. Some strainers, such as basket and Y-type strainers, are easy to clean and maintain, while others, such as cone strainers, require more time and effort to clean. Consider the frequency of cleaning required and the impact on downtime and production when selecting a strainer.
How Do Strainers Function in a Pipeline?
The primary role of strainers in a pipeline system is to capture any solid particles and debris that may be present in the fluid flow. As the fluid passes through the strainer, the screen or mesh catches the unwanted particles, allowing only the clean fluid to continue downstream.
The trapped particles build up over time, reducing the strainer’s efficiency and creating a pressure drop across the strainer. Once the pressure drop reaches a particular threshold, it becomes necessary to clean or replace the strainer. To maintain optimal flow and avoid damage to downstream equipment.
Overall, strainers play a critical role in protecting equipment, improving process efficiency, and ensuring the quality of the end product in many industries.
What are the Applications of Strainers in Piping in Industry?
Strainers have widespread usage in various industries, such as oil and gas, chemical, food processing, water treatment, and many others. The fundamental purpose of strainers in these industries is to safeguard downstream equipment from harm. And can result from unwanted solid particles, debris, and impurities that may accumulate in the fluid. Strainers are commonly utilized in various applications in piping systems, including:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Strainers are used to produce and transport oil and gas to remove solid particles, sand, and other debris. That can damage pipelines and equipment.
- Chemical Industry: In the chemical industry, strainers are used to remove impurities and solid particles from chemicals and other fluids. That is used in manufacturing processes.
- Food Processing Industry: Strainers are used in food processing applications to remove solid particles and debris from liquids, such as fruit juices, sauces, and syrups.
- Water Treatment Industry: Strainers are used in water treatment plants to remove solid particles and debris from incoming water, protecting downstream equipment such as pumps and valves.
- HVAC Industry: Strainers are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to remove dirt and debris from the air. That ensures efficient operation and prevents damage to equipment.
Overall, strainers play a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of piping systems across a range of industries. Helping to prevent downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure the quality of the end product.
Main Role Of Strainer In The Pipeline
Strainers are crucial components in pipeline systems as they help to filter out solid particles, debris, and other impurities. That can cause damage to downstream equipment, reduce efficiency, and compromise the quality of the end product. The presence of these contaminants can cause blockages, corrosion, and erosion of equipment, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
Strainers also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of piping systems. In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food and beverage, contaminants in the fluid can pose a significant risk to workers, the environment, and the end product. Strainers aid in reducing the risk of harm or contamination by eliminating particles and debris.
In addition, strainers can help prolong downstream equipment’s lifespan by preventing damage from particles and debris. This can lead to significant cost savings over time by reducing the need for repairs and replacements.
Overall, the role of strainers in a pipeline is to maintain the integrity and efficiency of the system. By removing unwanted contaminants and protecting downstream equipment.
Conclusion:
Strainers play a vital role in protecting downstream equipment, maintaining system efficiency, and ensuring product quality in various industries. Selecting the appropriate strainer for a specific application requires consideration of several factors, such as flow rate, pressure, temperature, particle size, and maintenance requirements. The correct strainer can help prevent damage to downstream equipment, minimize downtime, and save expenses. The five types of strainers in piping discussed in this guide are Y-strainers, basket strainers, duplex strainers, temporary strainers, and cone strainers, and each has unique features and benefits. By understanding the different types of strainers and their applications, individuals can make informed decisions. And select the right strainer for their specific needs.

[…] These are crucial components and the types of strainers in piping systems, that remove solid particles that can damage equipment or clog pipelines. […]
[…] and pressure conditions to prevent deformities or failure. Proper material selection enhances the efficiency and reliability of the strainer basket […]